Section 3.5.6: Patient Mediated Interventions
A O'Connor, RN, PhD, FCAHS
Professor, University of Ottawa
Senior Scientist, Ottawa Health Research Institute
Key Messages: Patient-Mediated Interventions
- Aim to actively engage patients to improve their knowledge, experience, service use, health behaviour, and health status
- Patient education and information improve knowledge; other outcomes improve with more specific and personalized information, and added professional and other support
- Research gaps: underlying frameworks, essential elements & duration, cost-effectiveness, best implementation strategies
Topics
- Case Study
- Effective Interventions
- Exemplars
1. Case Study
Mrs. C
"I've had a sleepless night… "
Knee pain affects sleep → not sure re surgery that was offered
Husband feverish → not sure re going to ER
Forgot to fill new script → not sure how important it is
Mrs. C Is Not Alone…
- 924 patients were questioned
- From 5 family practices in Quebec
- after making a decision with MD
| Unsure | Uninformed | Unclear Values | Unsupported | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOTAL | 55% | 15% | 7% | 38% |
| Vaccination | 71% | 29% | 36% | 36% |
| Diabetes | 60% | 20% | 0% | 27% |
| Pain | 59% | 14% | 10% | 31% |
| Depression | 58% | 15% | 5% | 30% |
| Hypertension | 57% | 17% | 5% | 40% |
| Lifestyle | 58% | 15% | 5% | 30% |
| Cholesterol | 55% | 18% | 18% | 27% |
Data from France Legare, U Laval
2. Effective Interventions
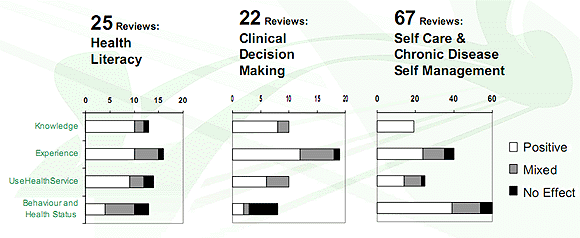
Effectiveness of strategies for informing, educating, and involving patients
Angela Coulter and Jo Ellins
BMJ 2007;335;24-27
doi:10.1136/bmj.39246.581169.80
25 Reviews: Health Literacy Interventions
22 Reviews: Clinical Decision Making Interventions
67 Reviews: Self Care & Chronic Disease Self Management Interventions
Health Literacy
Definition
A person who is health literate is able to access, understand, evaluate, and communicate information as a way to promote, maintain and improve health in a variety of settings across the life course.
Expert Panel on Health Literacy. A Vision for a Health Literate Canada: Report of the Expert Panel on Health Literacy. Canadian Public Health Association, 2008.
Interventions
- Written health information materials (e.g. brochures)
- Alternative format resources (e.g. internet)
- Targeted approaches for disadvantaged groups with low health literacy (e.g., pictograms, videotape, interactive computer)
Clinical Decision Making
Interventions
- Communication skills training for clinicians
- Question prompts for patients and coaching to develop skills in preparing for a consultation, deliberating about options, and implementing change
- Patient decision aids: explain options, present probabilities benefits vs. harms, clarify features of options that matter most, and provide structured guidance in deliberation and communication
Self Care & Self Management Interventions
- Aim to improve people's practices in maintaining and managing their disease
- Self management education to help people cope with their disease and manage daily problems
- Self monitoring and self-administered treatment
- Self help groups and peer support
- Patient access to personal health information
- Patient-Centered tele-care
Decision Aids Reduce Rates of Discretionary Surgery
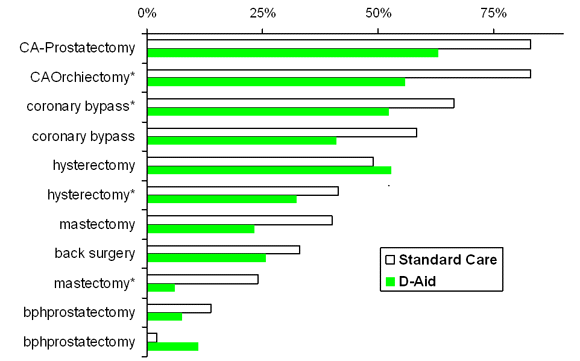
RR=0.76 (0.6, 0.9)
O'Connor et al., Cochrane Library, 2009
Review Conclusions
- Patient education/ information ↑ knowledge
- To ↑experience, service use, health outcomes, behaviour change…
- ↑ specificity/personalization of information
- combine interventions with professional or other social support
- extend duration for long term behaviour change
- Research gaps: underlying frameworks, essential elements & duration, cost-effectiveness, best implementation strategies
3. Exemplars




Challenge #1
- Need to train potential users:
- High school students
- Post secondary students
- Health science students
day 1 of training - New mothers
- Health departments
- Call centers and help-lines
Big Challenge #2
- Embed 'just in time' information for the individual as part of the process of care
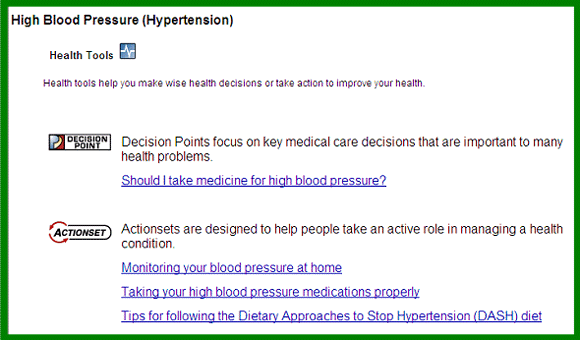
Wagner Chronic Care Model
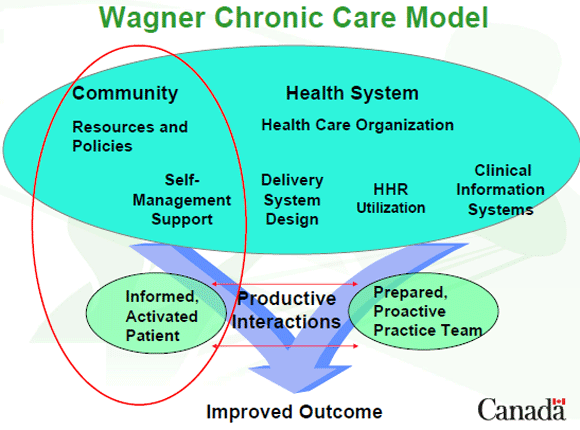
Implementation: Clinical Care
- Dartmouth HMC, VA, Mass Gen. & FIMDM Network
- Group Health Cooperative
- NHS Urology & Orthopedics
- Ottawa Pilot: Orthopedic Intake Clinic; Breast/Prostate Ca Center
Delivery Model
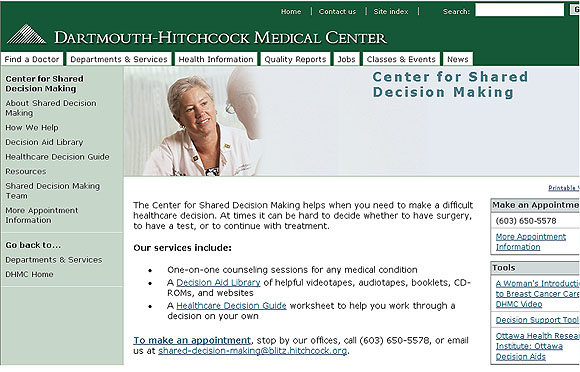
Decision Aid
Personal Decision Form
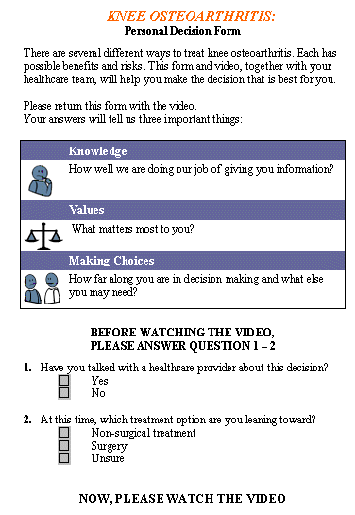
Summary Report for Surgeons
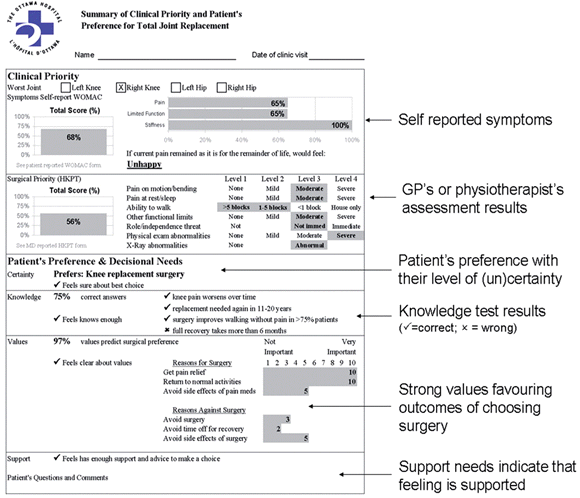
Stacey, D. et al. BMJ 2008;0:bmj.39520.701748.94v2-bmj.39520.701748.94
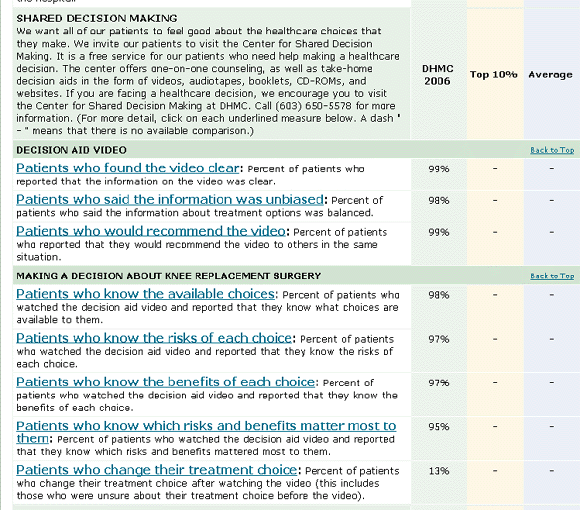
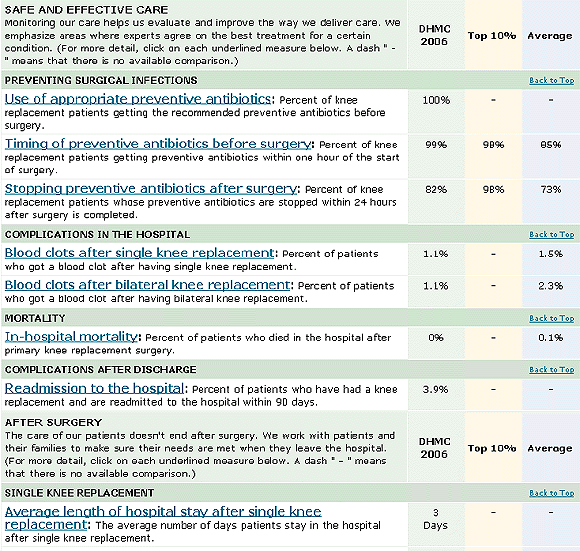
Online Quality Reports
Key Messages: Patient-Mediated Interventions
- Aim to actively engage patients to improve their knowledge, experience, service use, health behaviour, and health status
- Patient education and information improve knowledge; other outcomes improve with more specific and personalized information, and added professional and other support
- Research gaps: underlying frameworks, essential elements &s duration, cost-effectiveness, best implementation strategies
- Date modified: